Welcome to Jananam Fertility
Welcome to Jananam Fertility


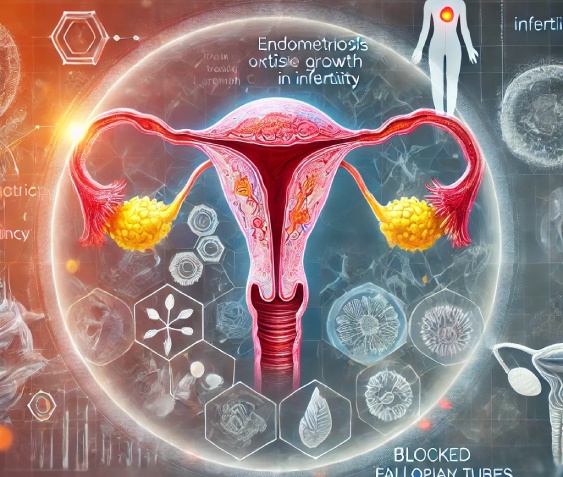
The overall prevalence of different menstrual problems was 60.61%, with dysmenorrhea (50.64%) being most common problem.
Book AppointmentWhen the menstrual cycle span abruptly deviates from the normal range (25-35 days), it is known as an irregular period. It is crucial that women are aware of the wide range of cycle length variations and how cycle duration alters with ageing. The traditional 28-day cycle is the most often observed cycle length, but variations from this duration can still be consistent with ovulation and good health. The length of menstruation might vary greatly as well.An irregular menstrual cycle is a defining feature of irregular periods (either missed, delayed, or intermittent).Amenorrhea is the temporary or permanent absence of menstruation. If it occurs before puberty, during pregnancy, when breastfeeding, or during menopause, it might be seen as normal.The absence of menstruation by the age of 16 in the presence of typical secondary sexual characteristics is known as primary amenorrhoea.Secondary amenorrhoea is the cessation of menstruation in a woman a period of six months who had previously experienced regular periods.The term used in medicine to describe painful periods is dysmenorrhoea.Menorrhagia: Increased discharge of the menstrual fluidIntermenstrual bleeding: Unusually heavy bleeding between periods (periods)
Some of the potential causes of irregular periods include the following: